The Evolution of SAP Analytics
There has been a proliferation of analytics platforms and tools in the market, trying to capture the analytical needs of business users. Still, the significant disruption in the area of analytics has just started to realize. Software vendors have been merging and acquiring niche companies with relevant capabilities to enhance their feature set within their platforms. SAP had been a laggard in the area of business intelligence and analytics in the past with tools like Business Explorer, and Web Application Designer couldn’t suffice most of the business needs. As a result, users started to jump ship with other reporting tools on top of the enterprise data warehouses.
With the advent of cheaper hardware components, consumer grade machine learning and predictive analytics on big datasets were brought within reach of the average business user. Due to this, the game of consolidation again surfaced in full force in the past few years, with several acquisitions and mergers taking place. Some of the major acquisitions were Google acquiring Looker, Salesforce acquiring Tableau, Sisense acquiring Periscope and the list goes on.
This time though, SAP invested in the existing Business Objects platform and capitalize on its core features while supplementing its capabilities with machine learning, planning, and predictive analytics. With the advent of in-memory computing with SAP HANA, SAP announced Project Orca in 2015. Internally codenamed Project Orca, SAP Analytics Cloud was formerly known as SAP Cloud for Planning, SAP Cloud for Analytics, and SAP BusinessObjects Cloud. This development of the unified and consolidated analytics solution started early in 2015 with the introduction of SAP Cloud for Planning. With its success, along with a rich roadmap, it became SAP Cloud for Analytics and has now been rebranded to SAP Analytics Cloud.
What is SAP Analytics Cloud?
SAP Analytics Cloud is a unified, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) that combines all the analytical capabilities with business intelligence, planning, machine learning, and predictive capabilities. It enables access to on-premise and cloud data sources with real-time and replicated data access, in one intuitive user interface, saving time and effort while making quick and informed decisions. It augments traditional analytics capabilities with conversational search features across all decision types, C-Suite to account clerk end-to-end decisions, a unified and scalable platform for data discovery, analysis, planning, and predictive analytics across all devices with data management and analytics together in one place to meet the needs of a diverse set of users across all decision types (strategic, operational, and tactical).
- Conversationally ask questions with instant results explained in natural language
- Detect drivers of a KPI and take the next best action using automated machine learning that discovers unknown relationships in data
- Predict potential outcomes and forecasts to enrich BI and planning
- Stories and dashboards on top of real-time live data connections enabling the users to explore data in real-time with Live connectivity while keeping the data within the corporate firewall
With SAP Analytics Cloud, SAP tried to cover all the aspects of the Analytics Ascendency Model positioning and branding it as an all-in-one platform:
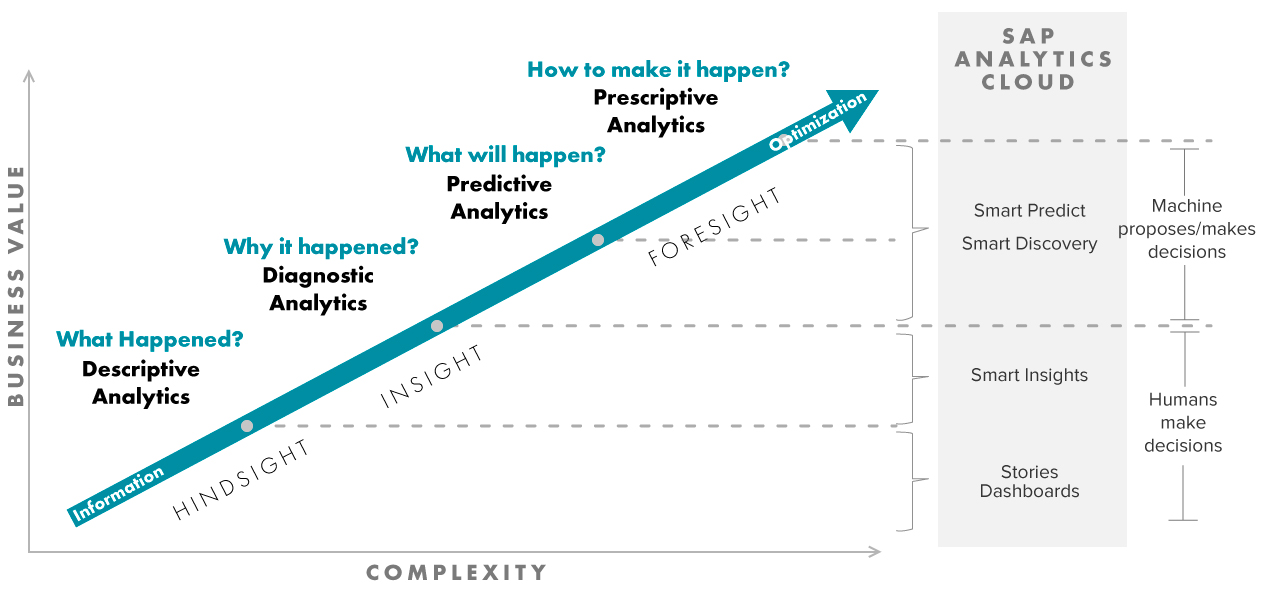
Inspired by Analytics Ascendency model by Gartner 2012
Will SAP win the business intelligence and analytics space back? How does it compare to its peers like Microsoft, Google, Salesforce, Qlikview? In the future posts we will analyze SAP Analytics Cloud’s readiness as an Enterprise BI and Analytics platform.



