Managing Custom Raw Materials for mRNA Production
Below, we dive into managing raw materials for mRNA production – the future of medicine. Read below for an overview of challenges using custom raw materials and strategies to mitigate or lessen the burden of using custom materials.
What is mRNA?
Messenger RNA (mRNA) was first discovered in the 1960s and has been in existence for decades. However, it was the coronavirus during the pandemic that brought mRNA into the spotlight with the development of the first mRNA vaccine.
In simple terms, mRNA is a molecule that carries instructions (genetic code) from the cell’s DNA (cell’s nucleus) to the cell’s watery interior (cytoplasm) to produce a specific protein (antibodies) that will help prevent or treat diseases. Our cells read the message and programs themselves to produce the protein – in essence, training our immune system to recognize and destroy infectious pathogens.
How is mRNA Produced?
Messenger RNA is made using DNA sequence as a base. The DNA sequence is made up of nucleotides, which is the combination of letters that make up a double DNA strand. Enzymes, the machinery of cells, “read” the DNA sequence and assemble an mRNA sequence made up of complementary nucleotides. The mRNA sequence is wrapped inside tiny bubbles of fat, called lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), that are then delivered into the cell. Once inside the cell, the mRNA sequence is used by other cellular machinery to produce the protein that helps treat or prevent a disease. Many of these materials used to manufacture and deliver mRNA are custom materials, which must be taken into consideration.
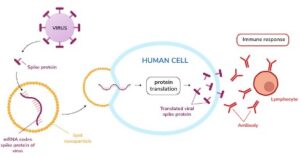
https://theconversation.com/what-is-mrna-the-messenger-molecule-thats-been-in-every-living-cell-for-billions-of-years-is-the-key-ingredient-in-some-covid-19-vaccines-158511
Custom Raw Materials in mRNA Production Manufacturing
To manufacture mRNA, one needs the following four main materials:
- DNA sequence template to make the protein (also known as plasmids)
- Nucleotides that comprise the mRNA
- Enzymes that assemble the mRNA
- Delivery materials (LNPs – lipid nanoparticles) to inject mRNA into our cells
While some of these materials can be purchased off the shelf in bulk, such as nucleotides, most materials, such as plasmids, enzymes and LNPs, are custom made.
Since every mRNA product targets a different protein, each mRNA sequence will require a different DNA template as a starting point, and these templates are all custom made. The enzymes used in the process may be purchased off the shelf, but process-specific demands may call for custom versions of the enzymes to achieve certain activity levels. Delivery materials (LNPs) may also be custom made, as each company will have their own approach for ensuring mRNA is delivered to the cells. One thing these materials have in common is that they require, at minimum, -20 C storage conditions.
Challenges using Custom Raw Materials
The most difficult aspect of producing mRNA products is the development and procurement of custom materials. The greater the number of custom materials, the more challenging it becomes to manufacture the final product. The lead time on custom GMP biologics can be extensive, reaching up to six or nine months from the time the order is placed until delivery. Custom GMP biologics can also be extremely expensive, costing tens of thousands of dollars for milligrams of material. Furthermore, manufacturer batch sizes can be constrained due to process considerations or manufacturer capacity. Forecasts may call for kilograms of material when manufacturers can only produce several hundred grams a year.
Packaging size should also be considered carefully. If freeze/thaw studies have not been performed on materials that must be stored at -20 C or below, containers must be for single use only. Examining the planned batch sizes and bill of material can guide decisions for how materials should be packaged for use to avoid waste and maximize usage and output.
Mitigation Strategies for mRNA Production
Here are some approaches that supply chain organizations can adopt to lessen the burden of using custom materials:
- Engage and qualify multiple suppliers for custom materials to help reduce manufacturer capacity constraints.
- Forecast manufacturing batches as far in advance as possible. Although there will be flux in the schedule, having visibility into upcoming batches will help suppliers prepare so they can meet custom raw material demand.
- Determine your risk tolerance for expiring materials. If the risk tolerance is high, over-order to ensure supply in the face of long lead times. If risk tolerance is low, be willing to modify the manufacturing scheduling to accommodate potential raw material shortfalls.
Looking Ahead
Messenger RNA has firmly established its existence as the future of medicine with the development and worldwide use of covid mRNA vaccine. Messenger RNA technology is a promising platform that offers faster and simpler methods for treating and preventing diseases. While there are many advantages to using mRNA, planning and procuring custom materials needed to manufacture mRNA remains one of the top concerns for companies. Companies can alleviate some of their angst by proactively implementing mitigation strategies that reduce overall risk and maximize productivity. For help with these mitigation strategies, reach out to our team at Clarkston today.
Subscribe to Clarkston's Insights
Contributions by Mike Lanewala



