Serialisation Challenges and Solutions Under the EU’s Falsified Medicines Directive
In 2008, the European Medicines Agency began discussing serialisation requirements for pharmaceutical manufacturers—if you’re unfamiliar with serialisation this video is helpful. In 2016, it officially adopted the Falsified Medicines Directive (FMD). The directive requires each pharmaceutical product sold in the EU to feature obligatory “safety features”. The safety features include, “a unique identifier and an anti-tampering device—to allow the verification of the authenticity of medicinal products subject to prescription and protect patients and business alike from the risks of falsified medicines.” The FMD is scheduled to launch in the first quarter of the calendar year 2019. However, pharmaceutical companies are required to connect their internal systems to the centralised EU data repository by February 9, 2019. Once connected, the data repository will contain the product master data and batch-specific information, enabling pharmacists and consumers the ability to authenticate their medicines at the point of dispensation.
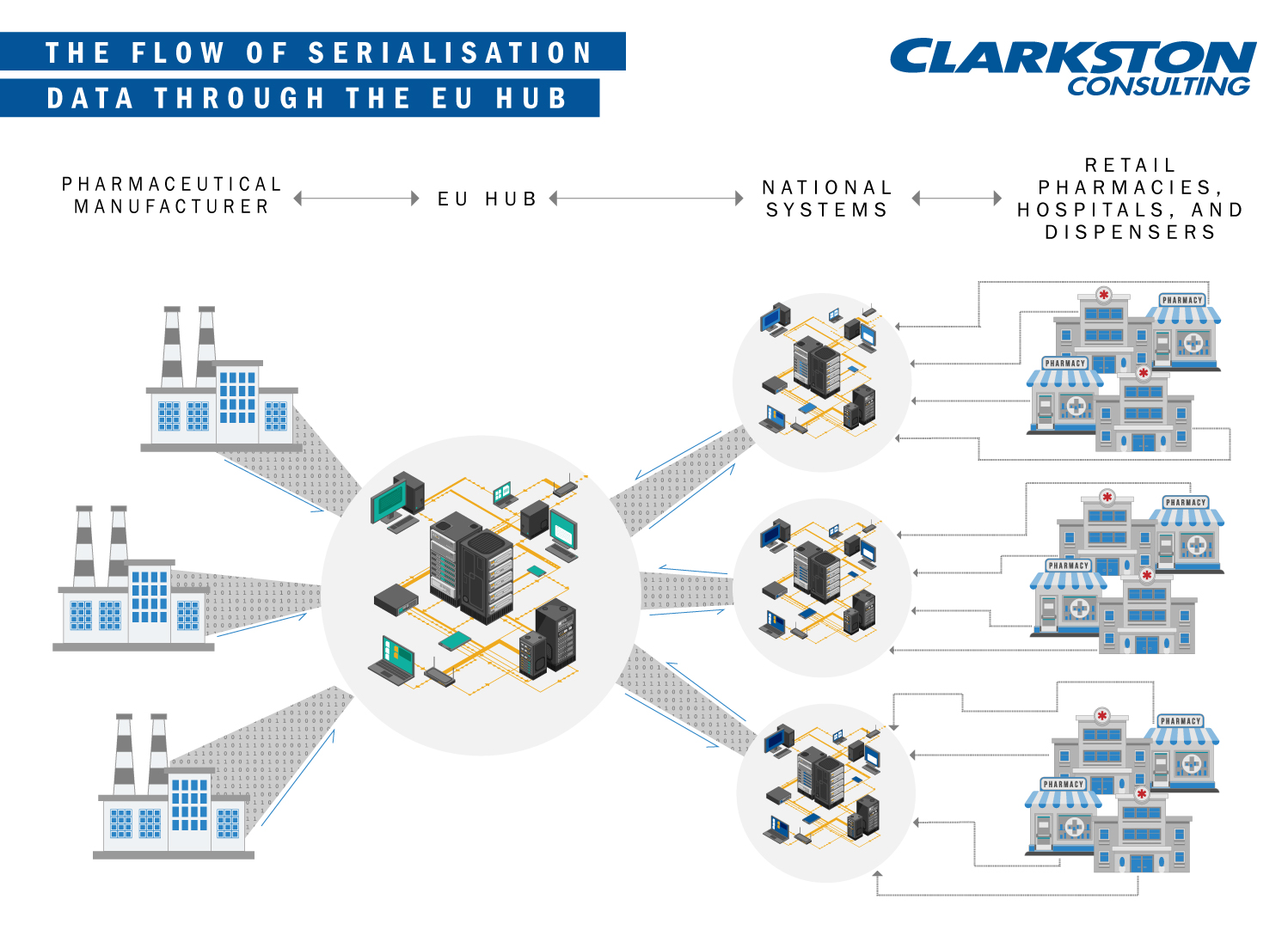
To meet this deadline, leaders must consider (1) Rigid Contractual Process, (2) Master Data, (3) Delayed National Medicines Verification Organisations, and (4) Impacts to Business Process.
Rigid Contractual Process
The European Medicines Verification Organisation (EMVO) is tasked with implementing FMD at a practical level. Given the large number of stakeholders the system requires (manufacturers, wholesalers, community pharmacists) EMVO has adopted a strict contractual onboarding process. In short, the process is time-consuming and rigid. For example, one of our clients requested minor changes to the required NDA and associated contracts. After 3 months the legal team was informed that no changes would be made.
Solution: Work closely with your Legal Department to help them understand EMVO will not make changes to the contract. Additionally, build extra time into the project plan for review.
Master Data
EMVO requires pharmaceutical manufacturers to supply a wide variety of complex master data. This data includes, but is not limited to regulatory, manufacturing, and logistical information. In a perfect world, this process would be seamless. However, most pharmaceutical manufacturers locate different data in different systems. Master data will likely be housed in their Level 4 Serialisation Solution (serialisation batch specific), ERP Systems (product master data), QRD Templates (regulatory), and eventually IDMP. The data must be consolidated to ensure a seamless integration.
Solution: Identify what systems the master data currently resides in, develop a strategy on how master data will be uploaded to the hub, and identify the right people to implement.
Delayed National Medicines Verification Organisations
Since many of the National Medicines Verification Organisations (NMVO) are currently under development and will not be live until mid-2018 and beyond, you may face additional complications even if your company is connected to the EU Hub prior to the February 2019 deadline.
For example, if you produce a serialised product for a market that is not ready, you will have to develop a solution to post the data after the fact. The original data transmission from the EU hub to the appropriate NMVO would fail. This requires attention to what batches are intended to be released before the systems are ready. One option is to refrain posting to the EU Hub at the time of shipment and to retroactively upload the master data. Now you may be thinking, well what about in the case of multi-market packs where one NMVO system is ready but the other is not? The full picture of the technical impacts is still to be determined, but it will likely require some reprocessing efforts and could cause systematical errors.
Solution: Identify products that will enter the market before the systems go-live and develop a plan on how data will be uploaded retrospectively.
Impacts to Business Process
As in any software implementation, business processes play a vital role in the FMD. Given the new system’s reach across distribution and production, everything from change management to logistics must be considered and accounted for.
For example, how will you handle:
- Split SKUs for countries that were previously multi-country batches?
- Triggers to determine when to send files to the correct NMVO?
- Relationships with logistics solutions providers to determine what serialisation activities they may provide?
Solution: Identify impacted processes and develop process maps, SOPs, and WPDs to support the new process.
Conclusion
With the 2019 deadline fast approaching, leaders at European pharmaceutical companies cannot afford to postpone FMD integration any longer. Given its scope, it will be an ambitious and complex project for all companies—regardless of size. In this article, we’ve identified four major considerations that should be answered before embarking on FDM integration. Very few of these considerations have easy or obvious solutions.
Solution: Our experience shows that a pilot programme is the best way to find the right answers while developing a repeatable process that can be rolled out to the larger organisation.



